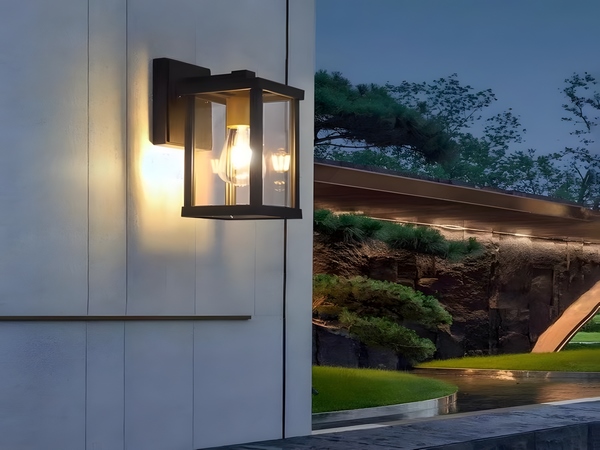

LED high mast lighting is installed outdoors, and due to the considerable height of high mast lights, they are significantly threatened by lightning strikes. If a high mast light is struck by lightning, it can cause considerable damage to both the lighting fixtures and the pole, leading to significant losses. The energy contained in a direct lightning strike is immense, with the voltage potentially reaching 5000kv, which possesses tremendous destructive power. Through years of practical research on high mast lights, it is understood that the general supply voltage for LED lights is typically 12v or 24v, which is classified as a safe voltage. However, measures need to be taken for lightning protection and grounding.
The main reasons for lightning strikes affecting LED high mast lights are as follows: Lightning current generates powerful electromagnetic waves, inducing extremely high pulse voltages on power and signal lines. When lightning current passes through electrical equipment, it generates substantial heat, potentially leading to fires or explosions. The frequent discharge between lightning cloud layers creates strong electromagnetic waves that cause common mode and differential mode interference, disrupting electrical equipment operation.
Currently, most LED high mast lights are predominantly made of conductive materials, effectively functioning as a lightning rod. Therefore, when a lightning strike occurs near the high mast light pole, if there are no other conductors higher than the pole in the vicinity, the pole itself can lead the lightning and disperse it underground through the lightning down conductor and grounding system, thus preventing equipment damage and personal safety incidents. Since LED high mast light poles are made of steel and hot-dip galvanized, the poles themselves can act as a down conductor. Additionally, the pole’s outer surface is coated with a plastic powder for a degree of surface insulation while maintaining electrical conductivity of the down conductor.

Overvoltage from switches in the power supply system of high mast lights, whether from inductive and capacitive loads being switched on or off or from short circuits in power lines, can generate high voltage pulses on the power lines, with pulse voltages reaching 3 to 5 times normal levels, potentially causing severe damage to equipment. The destructive effects are similar to those of a lightning strike.
The grounding system is made from 50*50*T5 hot-dip galvanized angle steel, with a length of 1875px. One end of the angle steel is sharpened for easy deep burial underground. The other end is welded with 50mm wide hot-dip galvanized flat steel, with the welding width being twice that of the flat steel width, and corrosion protection is applied at the welding point. The completed grounding device is vertically buried underground to a depth of 1m during the foundation construction of the high mast light. Once the pole is erected, the flat steel is welded to the flange of the high mast light pole, with the welding width being twice that of the flat steel width. After the installation of the high mast light is complete, a grounding resistance meter is employed to check if the lightning protection grounding meets the required standards.



